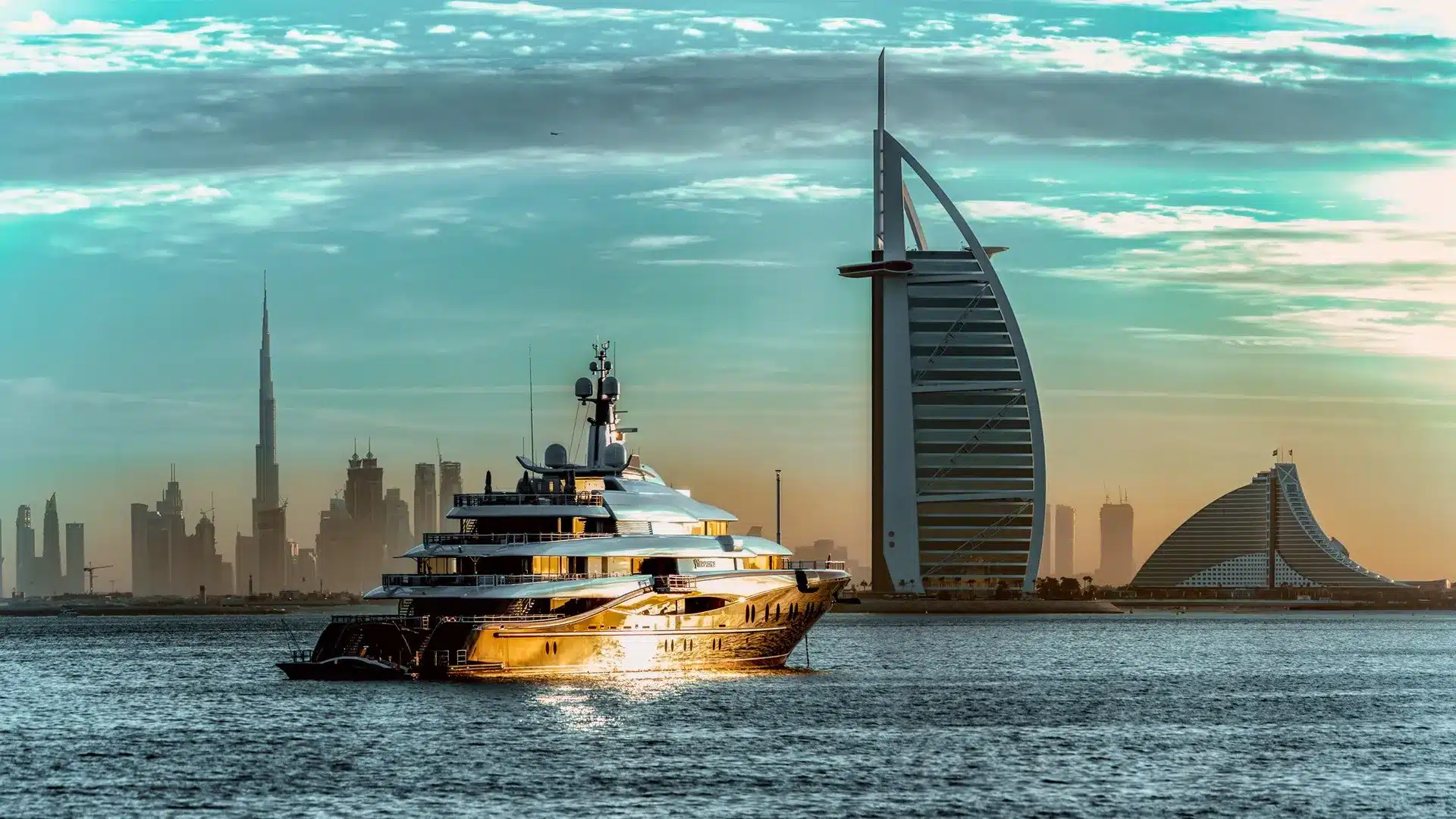
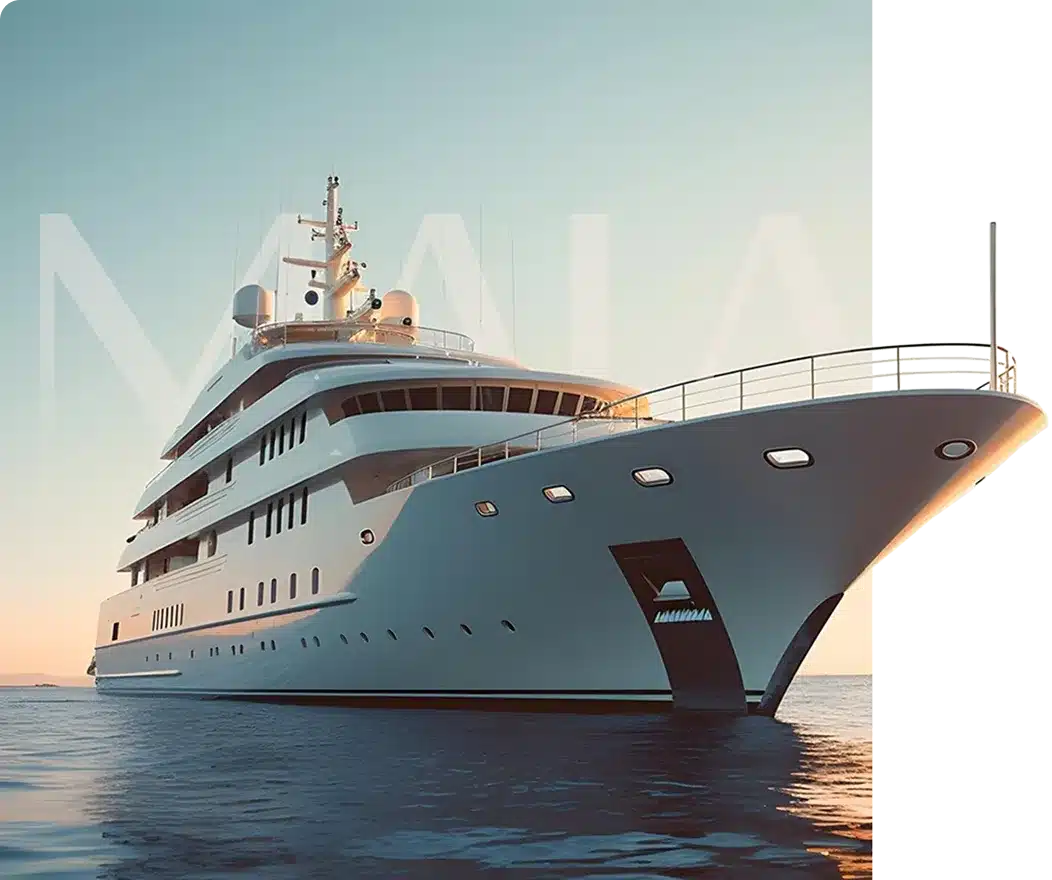
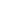
In the world of boating, different hull types offer unique advantages and characteristics. One such hull design is the displacement hull, which has been popular for centuries. In this article, we check out the fascinating world of displacement yachts, and their features.
So, are you ready? Let’s start
Displacement Hull Boat Definition
A displacement hull boat, also known as a displacement vessel or displacement craft, refers to a type of boat or ship that is designed to displace or push through the water rather than rise up on top of it. The hull shape and design of a displacement hull boat prioritize efficiency, stability, and comfort, making it well-suited for cruising at lower speeds and long-distance voyages.
Features of Displacement Yachts
Displacement yachts are synonymous with luxury, elegance, and fine craftsmanship. Designed for smooth, comfortable cruising, they have distinct features that set them apart from other types of yachts. Below are some of the most common features of displacement yachts:
Understanding Displacement Hulls
Displacement hulls are designed to displace water rather than rise on top of it. Unlike planing hulls that skim over the water’s surface at high speeds, displacement hulls excel at cruising efficiently at lower speeds.
The hulls typically have a long and narrow shape with a gentle curve, minimizing wake and resistance, allowing the yacht to move smoothly through the water.
Design Principles
The primary goal of displacement hulls is to minimize water resistance and maximize fuel efficiency. By creating a displacement wave that travels along the hull, these boats push through water rather than gliding on top, requiring less power.
Displacement yachts are generally longer and narrower compared to other yachts, a design that makes them more efficient over long distances.
Fuel Efficiency and Range
One of the major benefits of displacement yachts is their fuel efficiency. Due to their hull design, they require less energy to maintain speed, translating to reduced fuel consumption.
This efficiency makes them perfect for long-range cruising, where fuel economy is a priority. Displacement yachts can travel impressive distances without refueling, ideal for extended voyages.
Stability and Seaworthiness
Displacement yachts are known for their exceptional stability. Their long, narrow hulls and low center of gravity reduce rolling and pitching even in rough seas, making them ideal for ocean passages.
Their seaworthiness is one of their defining features, offering safety and comfort in various sea conditions, including challenging weather.
Comfort and Living Space
The shape of the displacement hull allows for spacious interiors with ample headroom and larger living areas. Yachts like trawlers and motor yachts with displacement hulls offer well-appointed cabins, saloons, and galleys.
These yachts are designed for extended cruising, with an emphasis on comfort, making them suitable for long stays onboard or even living aboard.
Serene and Relaxing Cruising Experience
Displacement yachts offer a calm and peaceful cruising experience. Their hull design results in minimal wake and noise, making for a quiet, serene ride.
Without the forces required for planing, they allow passengers to enjoy the tranquility of the open sea, perfect for those seeking a leisurely, relaxing boating experience.
Displacement Hull Design Like Cumbersome
While displacement hulls are efficient in slicing through water, they can be considered somewhat cumbersome due to their rounded, spherical shape. This shape enhances the hull’s ability to displace water effectively and provides a smooth ride.
The round shape allows for easy rolling, which can be both a benefit and a drawback in stormy conditions. Sailboats typically address this issue with a deep keel, adding stability and preventing excessive rolling in rough seas.
Weight of Displacement Hulls
Displacement yachts tend to be heavier than other types of yachts, relying on their buoyancy to stay afloat and move forward. The added weight contributes to their stability, making them less susceptible to the forces of wind and waves.
This heft is advantageous in challenging sea conditions, allowing the boat to continue moving steadily with less energy expenditure, much like a whale gracefully pushing through the water.
Types of Displacement Hulls
Displacement hulls can be further classified into different types based on their specific design features and intended purposes. Here are some common types of displacement hulls:
Full Displacement Yachts Hull
- Traditional and common type of displacement hull
- Designed to displace a volume of water equal to its own weight
- Long, narrow hull shape with a rounded or bulbous bow
- Optimized for fuel efficiency, stability, and long-range cruising at lower speeds
- Commonly found in trawlers, sailboats, and expedition yachts
Semi-Displacement Hull
- Combines elements of both displacement and planing hulls
- Features a flatter bottom section for partial lift at higher speeds
- Balances fuel efficiency at low speeds with the ability to achieve higher speeds when needed
- Typically found in motor yachts and cruisers that blend cruising and planing performance
Planing Hull
- Designed to ride on top of the water at high speeds
- Relies on dynamic lift and flatter bottom shape
- Achieves planing speeds rather than displacing water
- Common in speedboats, sport boats, and performance vessels
- Opposite of displacement hulls in terms of function and speed
Round-Bottom Hull
- Displacement hull with a smooth, curved bottom surface
- Provides a comfortable ride and excellent stability
- Known for gentle motion in the water, ideal for long-distance cruising
- Often used in sailboats, classic yachts, and certain motor yachts
Hard-Chine Hull
- Features distinct angular edges or chines along the sides
- Provides added stability and lift, enhancing performance
- Common in trawlers, power catamarans, and sport-fishing boats
- Offers fuel efficiency, stability, and good interior volume
Multihull Hulls
- Features multiple hulls, such as catamarans and trimarans
- Provides exceptional stability and spacious interiors
- Known for high cruising speeds and efficient use of space
- Popular among sailing enthusiasts and those seeking comfortable cruising experiences
Difference Between Displacement and Planing Yachts
Displacement Yachts:
- Move through water by displacing it
- Offer slower cruising speeds (8-12 knots) with fuel efficiency
- Prioritize comfort and stability for long-distance cruising
- Ideal for ocean crossings and long-range travel
Planing Yachts:
- Designed to rise and ride on the water surface at higher speeds
- Achieve speeds of 20 knots or more with powerful engines
- Offer dynamic, speed-oriented cruising experiences
- Tend to consume more fuel and have a shorter range than displacement yachts
Choice Factors:
Depends on user preference, intended usage, and desired cruising experience
Why Is a Longer Displacement Boat Hull Better?
A longer displacement hull is considered superior for several reasons:
Increased Stability:
A longer hull offers greater stability, especially in rough seas. It helps reduce rolling and pitching motions, ensuring a more comfortable ride for passengers.
Improved Handling:
Longer boats tend to have better handling characteristics. They are smoother to maneuver and provide more precise control, even at higher speeds.
Increased Interior Space:
A longer hull allows for more interior space, accommodating larger cabins, living areas, storage, and amenities. This is ideal for extended cruising and for hosting more guests.
Enhanced Performance:
Longer hulls often have better hydrodynamic efficiency. They create less drag, improving fuel efficiency. Additionally, they can achieve higher top speeds and better seakeeping abilities for smoother rides.
Longer Waterline Length:
A longer waterline length allows the boat to achieve higher speeds with less power. It improves fuel economy and enhances the overall cruising experience.
However, the optimal hull length depends on various factors, such as the type of boat and its intended use. Sailboats, motor yachts, and displacement yachts all have different design requirements, making hull length a variable feature based on the vessel’s purpose.
Why Is the Full Displacement Hull Shape the Most Seaworthy Boat Design?
The full displacement hull is considered one of the most seaworthy boat designs due to its characteristics:
Stability in Rough Seas:
Full displacement hulls displace a large volume of water, giving them inherent stability. This helps reduce rolling and pitching, making them safer and more comfortable in challenging sea conditions.
Smooth Ride:
The hull’s shape allows it to cut through water with minimal resistance. This results in a gentle, smooth ride, absorbing the impact of waves and providing comfort for passengers.
Fuel Efficiency:
Full displacement hulls are highly fuel-efficient, especially at lower speeds. They require less power to maintain steady motion, making them ideal for long-range cruising.
Long-Range Capabilities:
Due to their efficiency, full displacement hulls can cover vast distances without needing to refuel or restock. This makes them perfect for extended ocean crossings and long voyages.
Seakeeping Abilities:
Full displacement hulls are designed to handle various sea conditions. They cut through waves rather than riding on top of them, making them more stable and safer in rough seas.
This combination of stability, fuel efficiency, and range makes full displacement hulls ideal for serious ocean-going voyages and long-term cruising adventures.
How Quick Is Full Displacement Yachts?
Cruising Speed:
- Full displacement yachts typically cruise at slow speeds, around 6 to 8 knots.
- Their design requires them to displace a large volume of water before moving, contributing to their slower pace.
- Most displacement yachts lack the power to reach significantly higher speeds.
Advantages at Low Speeds:
- Perform well at lower speeds due to their lightweight and compact design.
- Require minimal energy for propulsion, which makes them fuel-efficient.
- Suitable for long-distance cruising and ocean crossings.
Hull Comparison:
- Displacement Hull: Submerged, buoyant hull designed to displace water.
- Planing Hull: Creates lift and floats on water, designed for higher speeds.
- Semi-Displacement Hull: Displaces at low speeds but partially lifts at higher speeds.
Buoyancy and Stability:
- The displacement hull floats on the surface of the water, balancing gravity’s downward pull and buoyancy’s upward force.
- This push-pull dynamic increases the yacht’s stability, making it better able to maintain its path.
- The Secret to Its Incredible MPG
Fuel Efficiency:
- Due to its efficient displacement of water, a full displacement yacht consumes less fuel compared to other hull types.
- It can carry a substantial load without significantly impacting fuel efficiency, making it ideal for transporting goods and long voyages.
Ride Comfort:
- Unlike planing hulls, which have rough rides until they reach higher speeds, displacement hulls offer a consistently smooth ride even at slow speeds.
- Planing hulls are better suited for speed but less comfortable in choppy waters.
Limitation: Top Speed of the Hull
- Displacement hulls have a natural maximum speed limitation, known as “hull speed.”
- No matter how powerful the engines or modifications, the yacht cannot exceed its maximum safe speed due to increased water resistance (drag).
Hull Speed Concept
- The maximum hull speed is directly proportional to the length of the yacht.
- As speed increases, more water must be displaced faster, increasing friction and making further acceleration difficult.
Maximum Hull Speed
- The point where drag becomes so great that the boat cannot move forward efficiently.
- Each displacement yacht has a maximum hull speed, determined by its length.
Example:
Imagine being towed behind a sailboat. As speed increases, the water resistance builds until you can no longer hold on. This illustrates the concept of reaching maximum hull speed.
Comparison with Planing Hulls
Planing Hulls vs. Displacement Hulls:
- Planing hulls create lift at certain speeds, allowing them to travel faster by riding on top of the water.
- Displacement hulls remain submerged, prioritizing stability and efficiency over speed.
Who Might Enjoy This Displacement Hull?
Ideal for Long-Range Cruising:
- Displacement hulls are best for those prioritizing range, safety, and comfort over speed.
- They offer the smoothest ride, making them suitable for ocean crossings and extended voyages.
- Their cruising speed may be slower (6-8 knots), but their stability and fuel efficiency are unmatched.
- Designed for life onboard and extensive travel, making them perfect for ocean crossings and exploration.
Displacement Hulls: The Pros and Cons
There are benefits and drawbacks to displacement hull design, just like any other. I’ll quickly go through each of them below.
Advantages
- Capable of withstanding stormy seas
- Not easy to capsize enjoy a gliding trip
- Low energy use despite high payload capacity: highly effective, very trustworthy, may be quite heavy, and cover a lot of ground
Disadvantages
- Has a top hull speed, rolls easily, and may capsize without a keel; has a large draught with a keel.
Conclusion
There’s a good reason why displacement hulls have dominated the market for centuries: they’re the most effective. They are efficient and trustworthy. Those are two of the most valuable skills to have when at sea. Displacement yachts are the norm for sailboats, and while there are certain negatives, they are well outweighed when it comes to cruising. However, if speed is your first need, you should look into purchasing a vessel with either a planning hull or a semi-displacement hull.
Conclusion
There’s a good reason why displacement hulls have dominated the market for centuries: they’re the most effective. They are efficient and trustworthy. Those are two of the most valuable skills to have when at sea. Displacement yachts are the norm for sailboats, and while there are certain negatives, they are well outweighed when it comes to cruising. However, if speed is your first need, you should look into purchasing a vessel with either a planning hull or a semi-displacement hull.
FAQs
How fast can a displacement yacht go?
Displacement yachts are optimized for cruising at lower speeds, typically ranging from 8 to 12 knots, depending on the vessel’s size and design.
Are displacement yachts fuel-efficient?
Yes, displacement yachts are known for their fuel efficiency due to their design which minimizes resistance and allows them to cruise efficiently at lower speeds.
Are displacement yachts suitable for ocean crossings?
Yes, displacement yachts with their stability and seaworthiness are well-suited for ocean crossings, providing a comfortable experience even in rough sea conditions.
What is the advantage of a full displacement yacht over other hull types?
The advantage of a full displacement yacht is its superior stability, fuel efficiency, and long-range capabilities, making it ideal for leisurely cruising and extended voyages.
What is the difference between a displacement yacht and a planning yacht?
A displacement yacht is designed to displace water and cruise at lower speeds efficiently, while a planing yacht is built to rise up on top of the water and achieve higher speeds by planing on its hull.
Are displacement yachts more stable than other types of yachts?
Yes, displacement yachts are known for their exceptional stability due to their design principles and ballasting systems, minimizing rolling and pitching motions.
Can displacement yachts be customized?
Yes, many displacement yachts offer customization options, allowing owners to personalize the interior layout, design elements, and features according to their preferences.
Absolutely, displacement yachts often have spacious interiors and comfortable accommodations, making them ideal for those seeking a liveaboard lifestyle.
Can displacement yachts handle rough seas?
Yes, displacement yachts are designed to handle rough seas, offering a comfortable and stable ride even in challenging weather conditions.